As a certain statistic will be used as an unbiased estimator takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with academic style and authoritative tone, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
This discussion will delve into the concept of unbiased estimators, their role in statistical inference, and their applications in various real-world settings.
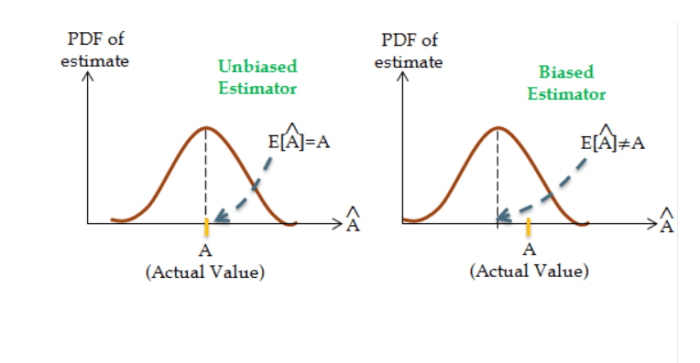
Unbiased estimators serve as a cornerstone of statistical analysis, providing a reliable basis for drawing inferences about a population from sample data. Their unbiased nature ensures that the expected value of the estimator is equal to the true population parameter, minimizing the risk of systematic errors.
Unbiased Estimators

In statistics, an unbiased estimator is a statistic that provides an accurate estimate of a population parameter, meaning that the expected value of the statistic is equal to the true value of the parameter.
Unbiased estimators are important because they provide a reliable way to make inferences about a population based on a sample. If an estimator is biased, then it will tend to overestimate or underestimate the true value of the parameter, which can lead to inaccurate conclusions.
Examples of Unbiased Estimators, A certain statistic will be used as an unbiased estimator
- The sample mean is an unbiased estimator of the population mean.
- The sample variance is an unbiased estimator of the population variance.
- The sample proportion is an unbiased estimator of the population proportion.
Statistical Inference
Unbiased estimators are used in statistical inference to make inferences about a population based on a sample. For example, we can use the sample mean to make inferences about the population mean, or we can use the sample variance to make inferences about the population variance.
One of the most important tools used in statistical inference is the confidence interval. A confidence interval is a range of values that is likely to contain the true value of a population parameter. Confidence intervals are constructed using unbiased estimators.
Examples of How Unbiased Estimators Are Used to Make Inferences About a Population
- We can use the sample mean to construct a confidence interval for the population mean.
- We can use the sample variance to construct a confidence interval for the population variance.
- We can use the sample proportion to construct a confidence interval for the population proportion.
Sampling Distributions
A sampling distribution is a probability distribution of all possible sample statistics that can be calculated from a given sample size. The sampling distribution of an unbiased estimator is centered around the true value of the population parameter.
The central limit theorem is a fundamental theorem of statistics that states that the sampling distribution of an unbiased estimator will be approximately normal, regardless of the shape of the population distribution, as long as the sample size is large enough.
Examples of How Sampling Distributions Are Used to Make Inferences About a Population
- We can use the sampling distribution of the sample mean to make inferences about the population mean.
- We can use the sampling distribution of the sample variance to make inferences about the population variance.
- We can use the sampling distribution of the sample proportion to make inferences about the population proportion.
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a statistical procedure used to test a hypothesis about a population parameter. Unbiased estimators are used in hypothesis testing to calculate the test statistic.
The p-value is a measure of the strength of the evidence against the null hypothesis. The p-value is calculated using the sampling distribution of the test statistic.
Examples of How Unbiased Estimators Are Used to Test Hypotheses About a Population
- We can use the sample mean to test a hypothesis about the population mean.
- We can use the sample variance to test a hypothesis about the population variance.
- We can use the sample proportion to test a hypothesis about the population proportion.
Applications of Unbiased Estimators
Unbiased estimators are used in a wide variety of applications in real-world settings, including:
- Medicine: Unbiased estimators are used to estimate the effectiveness of new drugs and treatments.
- Finance: Unbiased estimators are used to estimate the risk of investments.
- Education: Unbiased estimators are used to estimate the effectiveness of educational programs.
Unbiased estimators are a powerful tool that can be used to make informed decisions about a population based on a sample.
Questions and Answers: A Certain Statistic Will Be Used As An Unbiased Estimator
What is an unbiased estimator?
An unbiased estimator is a statistic whose expected value is equal to the true population parameter it estimates.
Why is it important to use unbiased estimators?
Using unbiased estimators minimizes the risk of systematic errors and ensures that the inferences drawn from sample data are reliable.
How are unbiased estimators used in statistical inference?
Unbiased estimators are used to construct confidence intervals and test hypotheses, allowing researchers to make inferences about a population based on sample data.