Which rationale explains the function of obsessions and compulsions? This question has puzzled researchers and clinicians for decades, and the answer is still not fully understood. However, there are several theories that attempt to explain why people with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) experience these symptoms.
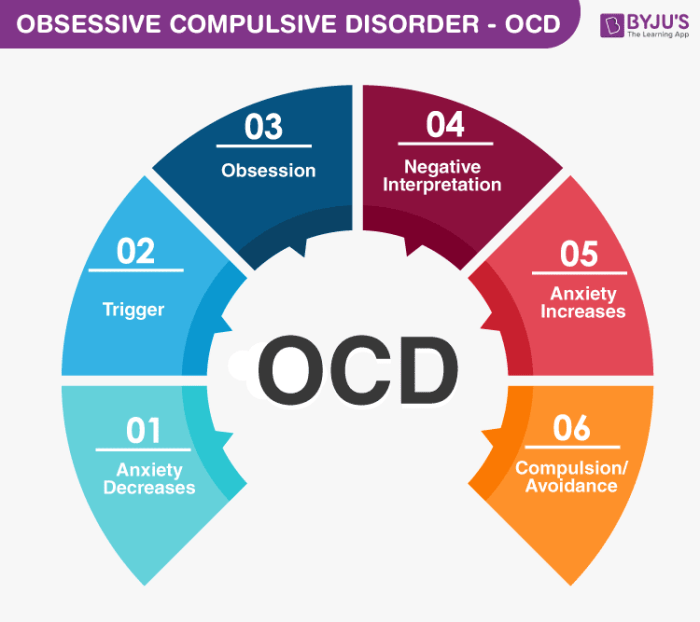
One theory is that obsessions and compulsions are a way of managing anxiety. People with OCD often experience intrusive thoughts that cause them anxiety or distress. These thoughts can be about anything, from fear of contamination to fear of harm.
Obsessions are repetitive thoughts or images that try to neutralize or suppress these intrusive thoughts. Compulsions are repetitive behaviors that people with OCD perform in an attempt to reduce their anxiety.
Definition of Obsessions and Compulsions

Obsessions are intrusive, unwanted, and distressing thoughts, images, or urges that repeatedly enter a person’s mind. They are often characterized by themes of contamination, harm, or perfectionism. Compulsions are repetitive, ritualistic behaviors or mental acts that an individual feels driven to perform in response to obsessions.
Compulsions are aimed at reducing anxiety or distress associated with obsessions and may include behaviors such as hand washing, checking, or repeating certain words or phrases.
Cognitive Functions of Obsessions
Obsessions can serve several cognitive functions. Firstly, they can help individuals manage anxiety and distress by providing a way to focus on specific thoughts or concerns. This can be seen as a form of distraction from other, more overwhelming or unpleasant thoughts or feelings.
Secondly, obsessions can provide a sense of control and predictability. By dwelling on specific thoughts or concerns, individuals may feel as if they are taking steps to prevent or prepare for potential threats.
Behavioral Functions of Compulsions
Compulsions are often performed to reduce anxiety or provide relief from the distress caused by obsessions. For example, an individual with contamination obsessions may engage in excessive hand washing to reduce their anxiety about germs. Compulsions can also provide a sense of completion or satisfaction, which can reinforce their performance.
Developmental and Cultural Influences
The development of obsessions and compulsions can be influenced by various factors, including genetics, childhood experiences, and cultural norms. Certain personality traits, such as perfectionism and anxiety sensitivity, have been linked to an increased risk of developing obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
Cultural factors can also play a role, as some cultures place a higher emphasis on cleanliness and order, which may contribute to the development of OCD symptoms.
Neurobiological Basis
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Neurobiological research has identified several brain regions and neurotransmitters that are involved in the development and maintenance of OCD. These include the orbitofrontal cortex, anterior cingulate cortex, basal ganglia, and serotonin.
Treatment Approaches, Which rationale explains the function of obsessions and compulsions
The primary treatment for OCD is cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which focuses on changing the thoughts and behaviors that maintain the disorder. CBT techniques include exposure and response prevention (ERP), which involves gradually exposing individuals to the feared stimuli while preventing them from performing compulsions.
Medication, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can also be used to treat OCD symptoms.
FAQ Overview: Which Rationale Explains The Function Of Obsessions And Compulsions
What are obsessions and compulsions?
Obsessions are repetitive thoughts or images that cause anxiety or distress. Compulsions are repetitive behaviors that people perform in an attempt to reduce their anxiety.
What is the function of obsessions and compulsions?
There are several theories that attempt to explain the function of obsessions and compulsions. One theory is that they are a way of managing anxiety. Another theory is that they are a way of gaining control over one’s environment.
What are the treatments for obsessions and compulsions?
There are a variety of treatments for obsessions and compulsions, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, medication, and exposure and response prevention.