In macroeconomics we study the interactions of three markets – In macroeconomics, we study the interactions of three markets: the goods and services market, the money market, and the foreign exchange market. These markets are interconnected and influence each other in complex ways, shaping the overall macroeconomic landscape.
Understanding these market interdependencies is crucial for policymakers and economists seeking to manage economic growth, inflation, and employment levels effectively.
Market Interactions: In Macroeconomics We Study The Interactions Of Three Markets

In macroeconomics, we delve into the intricate web of interactions that connect various markets within an economy. These markets are not isolated entities but rather operate in a dynamic interplay, influencing and being influenced by each other. Understanding these interdependencies is crucial for comprehending the overall functioning of an economy.
Consider the housing market. A surge in demand for housing can lead to increased construction activity, which in turn boosts the demand for building materials and labor in the construction sector. This surge can ripple through the economy, creating jobs and stimulating economic growth.
Conversely, a downturn in the housing market can have the opposite effect, leading to a decline in construction activity and reduced demand for related goods and services.
Types of Markets
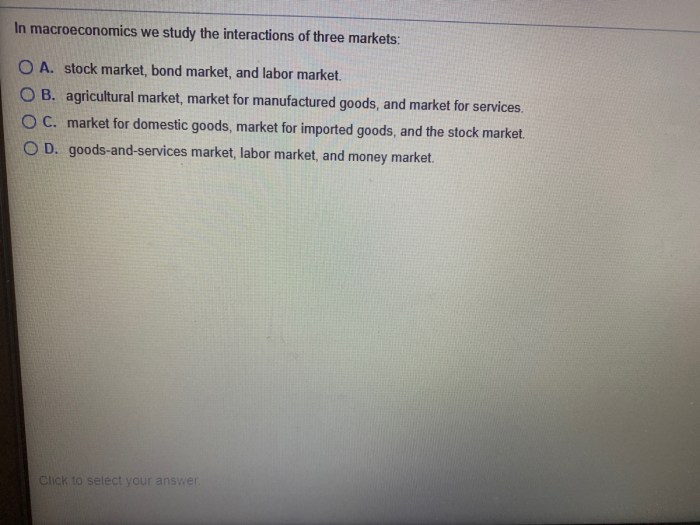
Macroeconomics primarily focuses on three fundamental markets:
- Goods and Services Market:This market encompasses the exchange of physical goods and intangible services between consumers and producers. It determines the prices and quantities of goods and services produced and consumed.
- Financial Market:This market facilitates the flow of funds between borrowers and lenders. It includes markets for stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments that channel savings and investments into productive activities.
- Labor Market:This market involves the interaction between employers and employees, determining wages, employment levels, and working conditions. It plays a vital role in determining the overall productivity and competitiveness of an economy.
| Market Type | Role | Key Variables |
|---|---|---|
| Goods and Services | Exchange of physical and intangible goods | Prices, quantities |
| Financial | Flow of funds between borrowers and lenders | Interest rates, asset prices |
| Labor | Interaction between employers and employees | Wages, employment, working conditions |
Equilibrium in Markets

Equilibrium in macroeconomic markets occurs when the quantity of a good or service supplied equals the quantity demanded. This equilibrium point is determined by the interaction of supply and demand forces. At equilibrium, there is no tendency for prices or quantities to change.
For instance, in the housing market, equilibrium occurs when the number of houses built matches the number of houses that buyers are willing and able to purchase at a given price. This equilibrium price balances the interests of both buyers and sellers, ensuring that the market operates efficiently.
FAQ Insights
What is the role of the goods and services market in macroeconomics?
The goods and services market determines the overall level of economic activity, including production, consumption, and investment.
How does the money market affect the economy?
The money market influences interest rates, which in turn impact borrowing, investment, and economic growth.
What is the significance of the foreign exchange market in macroeconomics?
The foreign exchange market facilitates international trade and investment, affecting exchange rates and the overall balance of payments.
