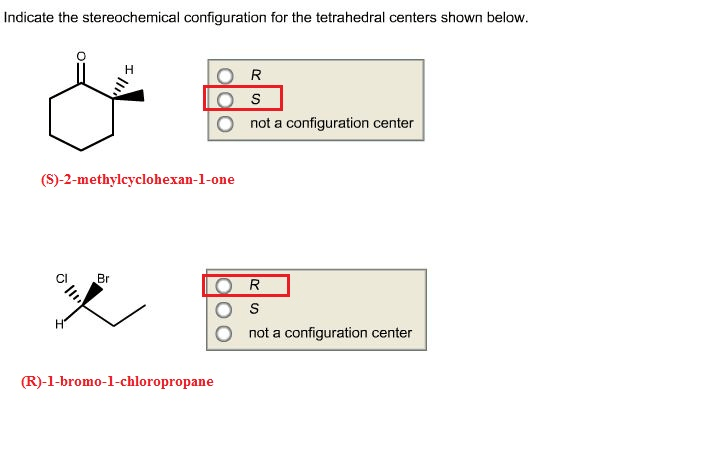
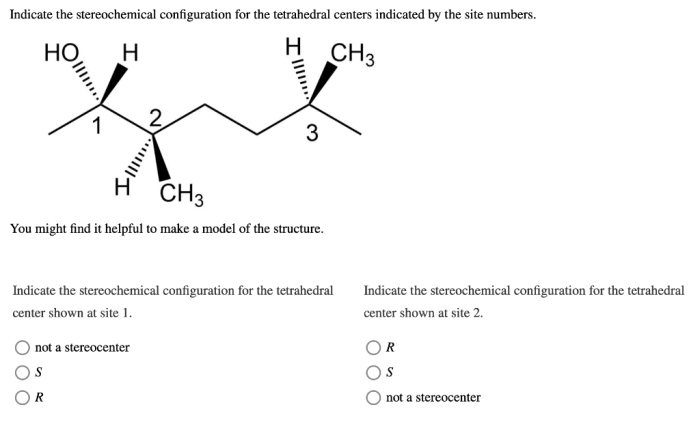
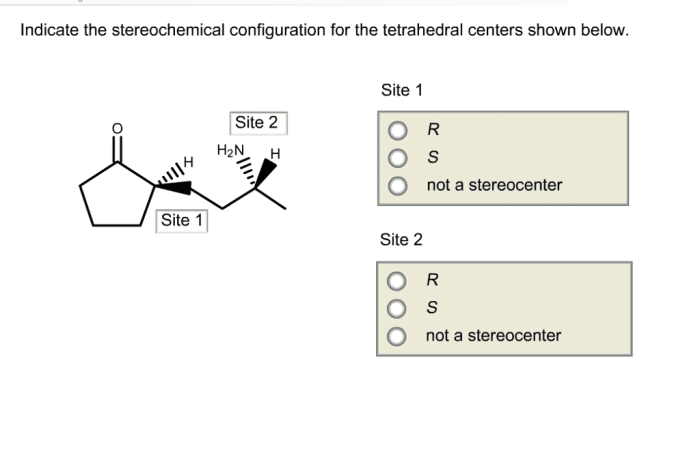
Indicate the stereochemical configuration for the tetrahedral centers – Indicating the stereochemical configuration for tetrahedral centers is a crucial aspect of understanding the three-dimensional structure and properties of molecules. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the concept, methods, and significance of stereochemistry in various fields.
Stereochemistry deals with the spatial arrangement of atoms and groups within molecules, and tetrahedral centers are carbon atoms bonded to four different substituents. The stereochemical configuration of these centers determines the molecule’s three-dimensional shape and its interactions with other molecules.
Stereochemistry of Tetrahedral Centers: Indicate The Stereochemical Configuration For The Tetrahedral Centers
Stereochemistry is the study of the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms and groups in molecules. It plays a crucial role in understanding the structure and properties of molecules, particularly those with tetrahedral centers.
Tetrahedral centers are carbon atoms with four different substituents. The stereochemical configuration of a tetrahedral center refers to the spatial arrangement of these substituents.
Indicating Stereochemical Configuration
The stereochemical configuration of tetrahedral centers is indicated using the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) priority rules. These rules assign priorities to the substituents based on their atomic number and the number and type of atoms bonded to them.
The substituent with the highest priority is assigned the letter R (for rectus), while the substituent with the lowest priority is assigned the letter S (for sinister). The remaining two substituents are assigned the letters R or S based on their relative positions.
Stereochemical Relationships, Indicate the stereochemical configuration for the tetrahedral centers
Enantiomers are molecules that are mirror images of each other. They have the same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in the spatial arrangement of their atoms.
Diastereomers are molecules that are not mirror images of each other. They have the same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in the spatial arrangement of their atoms.
Importance of Stereochemistry
Stereochemistry is of great importance in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, biochemistry, and materials science.
In pharmaceuticals, the stereochemistry of a drug molecule can affect its biological activity and toxicity. For example, the enantiomers of the drug thalidomide have different effects: one enantiomer is an effective sedative, while the other causes birth defects.
FAQ Resource
What is the significance of stereochemistry in drug development?
Stereochemistry plays a critical role in drug development as it affects the biological activity and efficacy of drugs. Enantiomers, molecules that are mirror images of each other, can have different pharmacological properties and side effects, necessitating careful consideration of stereochemistry during drug design and synthesis.
How can we determine the stereochemical configuration of a tetrahedral center?
The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) priority rules provide a systematic method for assigning priorities to the substituents attached to a tetrahedral center. These priorities determine the stereochemical configuration, which can be designated as R (rectus) or S (sinister).
What are the different types of stereoisomers that can exist for molecules with multiple tetrahedral centers?
Molecules with multiple tetrahedral centers can exhibit various types of stereoisomers, including enantiomers, diastereomers, and meso compounds. Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images, while diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not mirror images. Meso compounds are achiral molecules that have an internal plane of symmetry, making them superimposable on their mirror images.